By admin / 26 Sep 2025
In the world of engineering and mechanical systems, couplings play a vital role in connecting two rotating shafts, enabling smooth power transmission, reducing vibration, and protecting equipment from damage. Whether in manufacturing plants, automotive systems, or heavy industrial machinery, couplings are essential for reliable operation and efficiency.
A coupling is a mechanical device used to connect two shafts together at their ends to transmit power. Its primary functions include:
Couplings can be either rigid (providing a solid connection with no flexibility) or flexible (allowing some movement to accommodate misalignment or vibration).
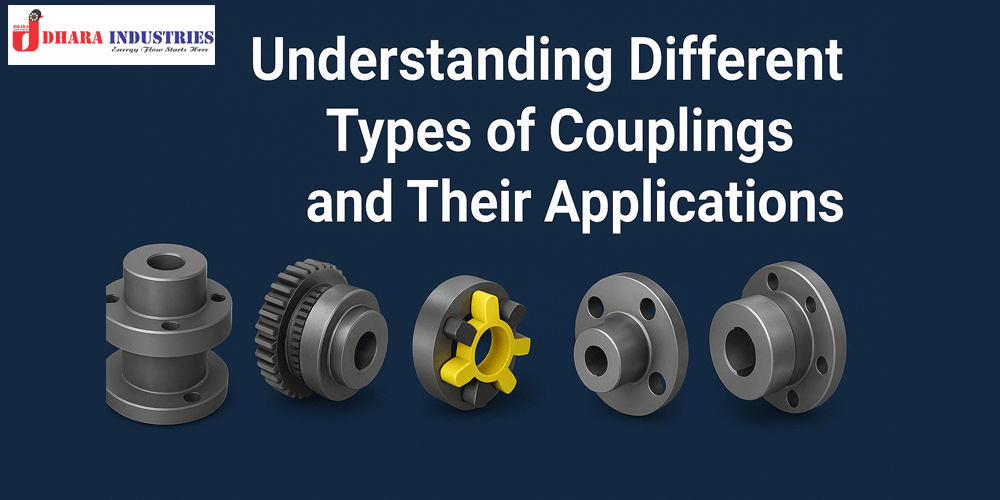
There are numerous types of couplings available, each designed for specific mechanical requirements. Let’s look at the most commonly used ones.
Rigid couplings are used when precise shaft alignment is required. They do not allow for misalignment or flexibility.
Examples of rigid couplings:
Applications:
Advantages:
Limitations:
Flexible couplings allow for slight misalignments between connected shafts while still transmitting power. They help reduce vibration and shock loads.
Examples of flexible couplings:
Applications:
Advantages:
A fluid coupling, also known as a hydraulic coupling, uses a liquid medium (typically oil) to transmit torque. Working Principle:
The driving shaft (pump impeller) transfers energy to the fluid, which in turn transmits it to the driven shaft (turbine runner).
Applications:
Advantages:
Limitations:
A gear coupling consists of two hubs with external gear teeth connected by a sleeve with internal gear teeth.
Applications:
Advantages:
Limitations: